ZYTIGA® Dosing & Monitoring
HOW TO TAKE ZYTIGA® (abiraterone acetate)

- ZYTIGA® tablets must be taken as a single dose once daily on an empty stomach. Do not eat food 2 hours before and 1 hour after taking ZYTIGA®
- ZYTIGA® should not be taken with food. ZYTIGA® taken with food causes increased exposure and may result in adverse reactions

- Tablets should be swallowed whole with water
- Tablets should not be crushed or chewed
- Patients should also receive a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog concurrently or should have had bilateral orchiectomy
THE RECOMMENDED DOSE OF ZYTIGA®
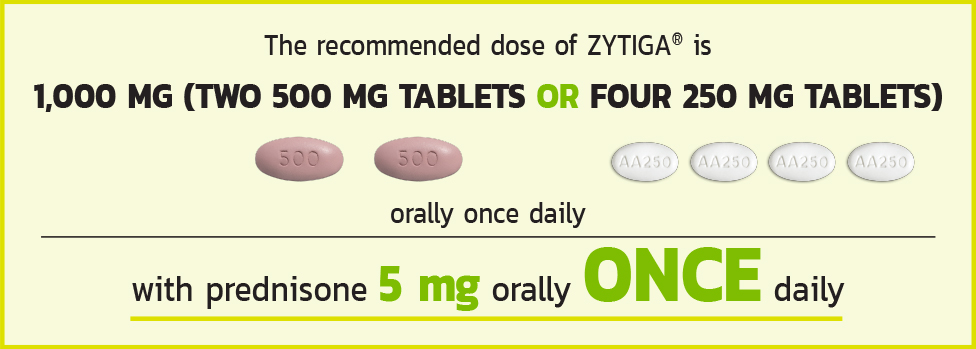
Tablets shown are not actual size.
Drugs That Inhibit or Induce CYP3A4 Enzymes - Based on in vitro data, ZYTIGA® is a substrate of CYP3A4. In a drug interaction trial, co-administration of rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, decreased exposure of abiraterone by 55%. Avoid concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducers during ZYTIGA® treatment. If a strong CYP3A4 inducer must be co-administered, increase the ZYTIGA® dosing frequency only during the co-administration period [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. In a dedicated drug interaction trial, co-administration of ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4, had no clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of abiraterone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Effects of Abiraterone on Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes - ZYTIGA® is an inhibitor of the hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes CYP2D6 and CYP2C8. Avoid co-administration with CYP2D6 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index. If alternative treatments cannot be used, consider a dose reduction of the CYP2D6 substrate drug. In a CYP2C8 drug interaction trial in healthy subjects, the AUC of pioglitazone, a CYP2C8 substrate, was increased by 46% when administered with a single dose of ZYTIGA®.
Patients should be monitored closely for signs of toxicity related to a CYP2C8 substrate with a narrow therapeutic index if used concomitantly with ZYTIGA® [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
For more information on Dose Modification Guidelines in Hepatic Impairment and Hepatotoxicity and information on Dose Modification Guidelines, see When To Modify Dose.
THE ROLE OF PREDNISONE
Co-administration of Prednisone Supresses Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Drive, Reducing the Incidence and Severity of Mineralocorticoid-Related Adverse Reactions1
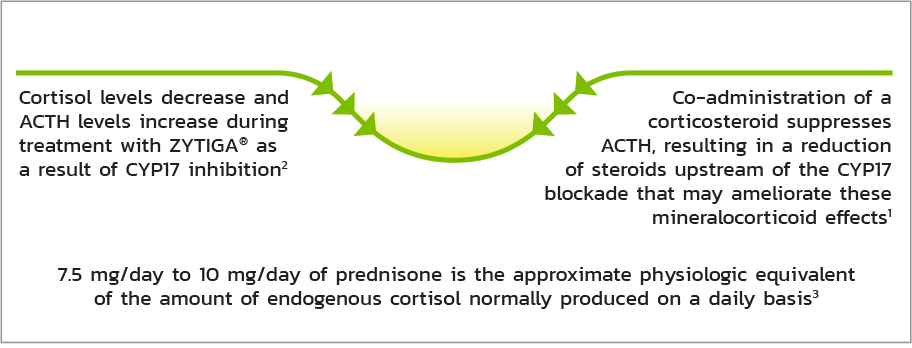
Adrenocortical Insufficiency - Adrenocortical insufficiency was reported in patients receiving ZYTIGA® in combination with prednisone, after an interruption of daily steroids and/or with concurrent infection or stress. Monitor patients for symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency if prednisone is stopped or withdrawn, if the prednisone dose is reduced, or if the patient experiences unusual stress. Symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency may be masked by adverse reactions associated with mineralocorticoid excess seen in patients treated with ZYTIGA®. Perform appropriate tests, if clinically indicated, to confirm adrenocortical insufficiency. Increased dosages of corticosteroids may be used before, during, and after stressful situations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
MONITORING CONSIDERATIONS
Schedule for Required Monitoring of Patients Receiving ZYTIGA® Plus Prednisone
| Assessment | Frequency* |
| Hypertension, hypokalemia, and fluid retention | Baseline and at least once a month |
| Liver function tests (ALT, AST, bilirubin) | Baseline and every 2 weeks for the first 3 months of treatment and monthly thereafter† |
- Control hypertension and correct hypokalemia before starting and during treatment with ZYTIGA®
- Closely monitor patients whose underlying medical conditions might be compromised by increases in blood pressure, hypokalemia or fluid retention, such as those with heart failure, recent myocardial infarction, cardiovascular disease, or ventricular arrhythmia. In postmarketing experience, QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes have been observed in patients who develop hypokalemia while taking ZYTIGA®.
- Monitor patients for symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency if prednisone is stopped or withdrawn, if the prednisone dose is reduced, or if the patient experiences unusual stress.
- Permanently discontinue ZYTIGA® for patients who develop a concurrent elevation of ALT greater than 3 x ULN and total bilirubin greater than 2 x ULN in the absence of biliary obstruction or other causes responsible for the concurrent elevation.
- Promptly measure serum total bilirubin, AST, and ALT if clinical symptoms or signs suggestive of hepatotoxicity develop. Elevations of AST, ALT, or bilirubin from the patient’s baseline should prompt more frequent monitoring
- Monitor blood glucose in patients with diabetes during and after discontinuation of treatment with ZYTIGA®. Assess if antidiabetic drug dosage needs to be adjusted to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia.
- For more information on Dose Modification Guidelines in Hepatic Impairment and Hepatotoxicity and information on Dose Modification Guidelines for Strong CYP3A4 Inducers, see When To Modify Dose
* Assess more frequently as required.
† Suggested schedule for patients with no or mild baseline hepatic impairment. For patients with baseline hepatic impairment or who develop hepatotoxicity during treatment, see When to Modify Dose. Do not use ZYTIGA® in patients with baseline severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). Please see additional safety information below and full Prescribing Information for complete Dosage and Administration and Warnings and Precautions.
WHEN TO MODIFY DOSE
| No/Mild Hepatic Impairment | Moderate Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) Prior to treatment | Severe Hepatic Impairment (Child Pugh Class C) Prior to treatment |
| No dosage adjustment is necessary | Reduce ZYTIGA® dose to 250mg orally QD | Do not use ZYTIGA® in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) |
OD = once daily; BID= twice daily.
For patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) monitor serum transaminases (ALT [alanine aminotransferase] and AST [aspartate aminotransferase]) and bilirubin levels
- Prior to the start of treatment
- For the first month of treatment, monitor every week
- For the following 2 months of treatment, monitor every 2 weeks
- Monthly thereafter
If elevations in ALT and/or AST >5 x ULN (upper limit of normal) or total bilirubin >3 x ULN occur, discontinue ZYTIGA® and do not re-treat patients with ZYTIGA®.
Permanently discontinue ZYTIGA® (abiraterone acetate) for patients who develop a concurrent elevation of ALT greater than 3 x ULN and total bilirubin greater than 2 x ULN in the absence of biliary obstruction or other causes responsible for the concurrent elevation.
First occurrence of hepatotoxicity
- Patient develops hepatotoxicity during treatment with ZYTIGA®: ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and/or AST (aspartate aminotransferase) >5 x ULN (upper limit ofnormal) or total bilirubin >3 x ULN
- Withhold ZYTIGA® treatment and monitor LFTs*
- Patient's LFTs return to baseline levels or patient's AST and ALT ≤2.5 x ULN and total bilirubin ≤1.5 x ULN
- Resume ZYTIGA® at 750 mg once daily
- Monitor AST, ALT, and bilirubin at a minimum of every 2 weeks for 3 months and monthly thereafter
Recurrence of hepatotoxicity (at 750 mg dose)
- If hepatotoxicity recurs at 750 mg once daily:
- Withhold ZYTIGA® treatment and monitor LFTs*
- When patient's LFTs return to baseline levels or patient's AST and ALT ≤2.5 x ULN and total bilirubin ≤1.5 x ULN
- Resume ZYTIGA® at 500 mg once daily
*LFT: Liver Function Test.
Recurrence of hepatotoxicity (at 500 mg dose)
- If hepatotoxicity recurs at 500 mg once daily:
- Discontinue treatment with ZYTIGA®
The safety of ZYTIGA® re-treatment of patients who develop AST or ALT ≥20 x ULN and/or bilirubin ≥10 x ULN is unknown.
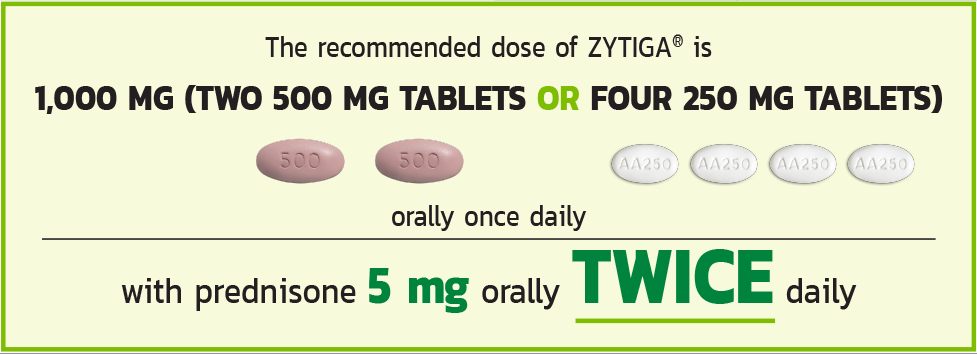
For patients taking strong CYP3A4 inducers
- Avoid concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducers (eg, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, phenobarbital) during ZYTIGA® treatment
- If a strong CYP3A4 inducer must be co-administered, increase the ZYTIGA® dosing frequency to twice a day only during the co-administration period (eg, from 1,000 mg once daily to 1,000 mg twice a day)
- Reduce the dose back to previous dose and frequency if the concomitant strong CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued
For patients taking CYP2D6 and CYP2C8 substrates
- Avoid co-administration of abiraterone acetate with substrates of CYP2D6 with a narrow therapeutic index (eg, thioridazine)
- If alternative treatments cannot be used, consider a dose reduction of the concomitant CYP2D6 substrate drug
- Patients should be monitored closely for signs of toxicity related to a CYP2C8 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index if used concomitantly with ZYTIGA®
References:1. Attard G, Reid AHM, A’HernR, et al. Selective inhibition of CYP17 with abiraterone acetate is highly active in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(23):3742-3748. 2. Attard G, Reid AHM, Yap TA, et al. Phase I clinical trial of a selective inhibitor of CYP17, abiraterone acetate, confirms that castration-resistant prostate cancer commonly remains hormone driven. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(28):4563-4571. 3. Krasner AS. Glucocorticoid-induced adrenal insufficiency. JAMA. 1999;282(7):671-676.
